28.11.2019
We are in the plain of Gioia Tauro where the “Struncatura” has risen after being for a long time an illegal recovery pasta.
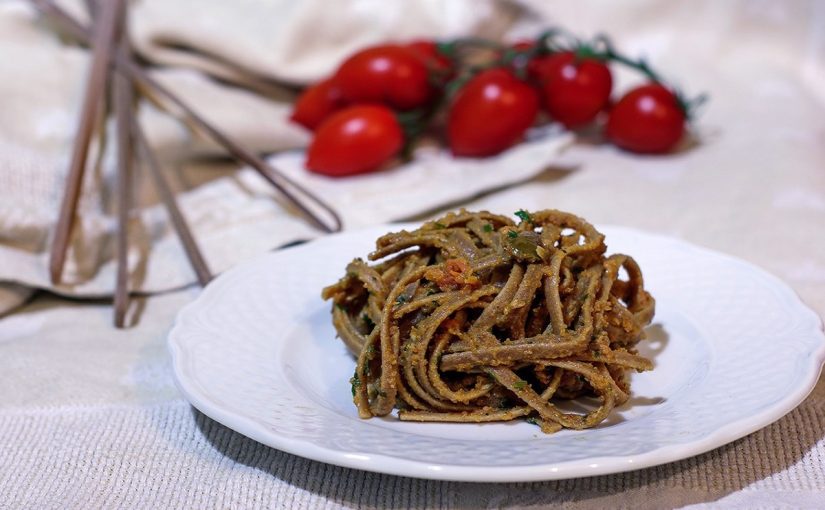
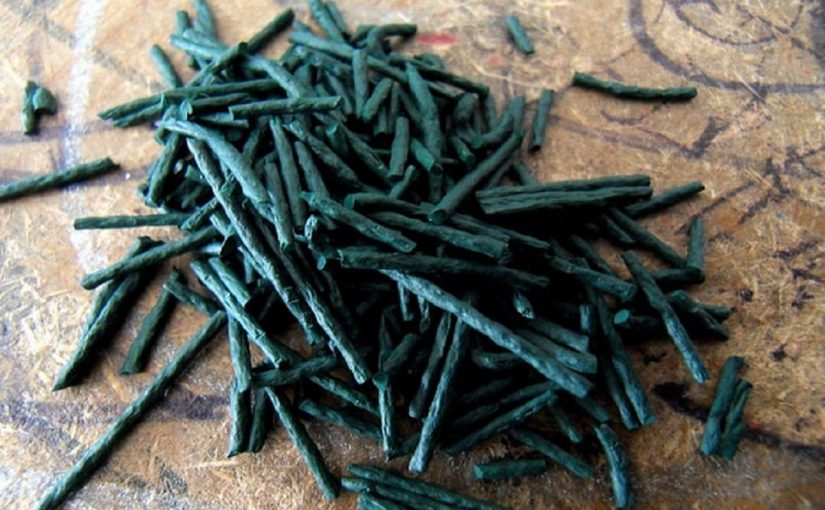
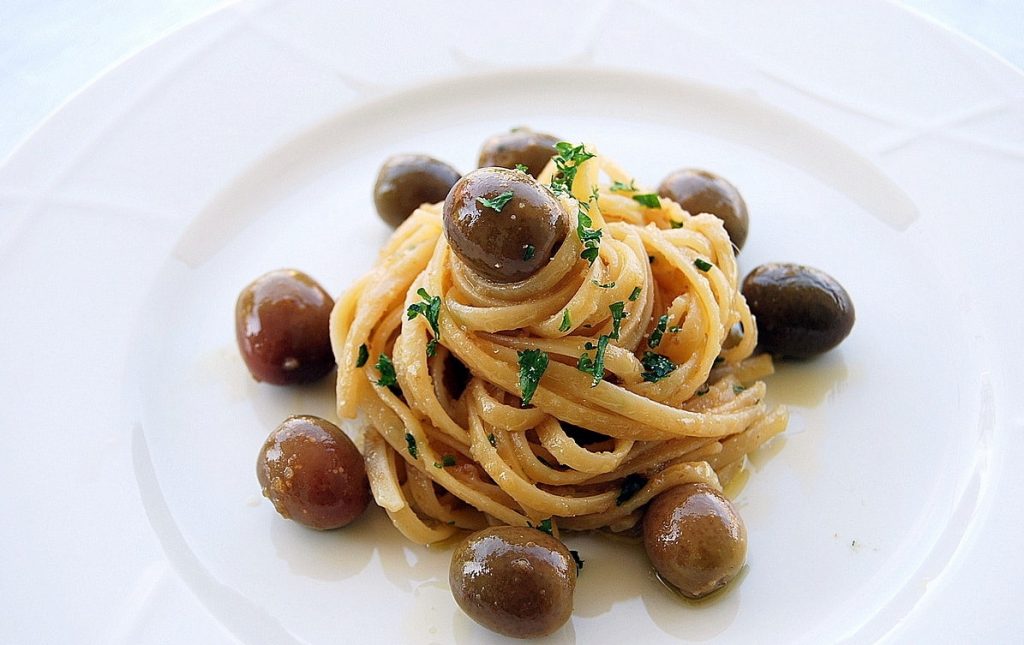
Calabrian Struncatura arrived in Gioia Tauro in 1919, brought from Atrani, a village on the Amalfi Coast. An inexperienced eye can confuse it with a simple whole wheat pasta, but a Calabrian from the province of Reggio recognizes it at first glance. Dark, porous and rough linguine: this is how the Struncatura (Italianized, “Stroncatura“) presents itself, a symbol of the gastronomic identity of a part of Calabria.

The Calabrians are great eaters of pasta, but unlike the “fileja” (a kind of strozzapreti made with flour, water) diffused almost everywhere, the Struncatura is available only in the province of Reggio Calabria and the production area is restricted to such area.

Many years ago there was no law governing whole wheat pasta, it had no label and was not legal. It could be sold only smuggled, just under the table to the people known.
THE TERRITORY OF STRUNCATURA
The place of Struncatura is the plain of Gioia Tauro, the second largest plain in the region, enclosed between the Tyrrhenian Sea, Monte Poro and Aspromonte. A fertile agricultural center, rich in citrus groves and ancient olive trees, whose fame unfortunately is also connected to sad episodes of ‘ndragheta and caporalato.
The two main cities, Gioia Tauro and Palmi, compete for the paternity of the Struncatura, but if you want to eat the real one, you have to go to Gioia Tauro.
In Gioia Tauro one hundred years ago the Struncatura was brought to the this city, making it the culinary center of the whole Plain.

Struncatura arrived in Gioia Tauro in 1919, as said above, brought directly from Atrani, a village on the Amalfi Coast. Some merchants came to Gioia because, at the time, the town was an important merchant artery. Nobody knew Struncatura here, it was a pasta that was made only in Campania, using the various durum wheat semolina that advanced in the sacks of pasta factories.
THE PRESENT OF THIS PASTA
Today the Struncatura is in great demand, even as an ingredient in starred restaurants, especially in Calabria, but its appeal has not always been recognized. Rather. There was a time when this pasta was synonymous with pet food or poor cooking.
Nowadays, the ingredients are always the same: Italian durum wheat, semolina (from Campania, Puglia, Basilicata and Lazio) and water. Semolina, not flour. It is not the same thing and the flour is not among the components of this pasta.

To make the Struncatura it shall be used, in particular, the parts of the durum wheat that are less sugary and richer in fiber, the bran and the endosperm. This affects the color of the dough, made porous and rough by the slow drying.
In the past, given that this pasta was synonymous with pet food and poor cooking, in order to cover its acidity, it was often seasoned with sardines and anchovies which, with their strong flavor, were intended to suppress its taste without compromise.
Still today, the dough retains cooking in an exceptional manner, and the porosity retains a savory, but not intrusive, seasoning, in which it can be added anchovy and the chili pepper, plus some olives.

Its re-discovery, however, led to an unbridled race to production with unsuccessful attempts to replicate it, which resulted in the frequent opening of pasta factories, not always up to par, not very respectful of the raw material. So it often happens that you come across culinary oxymorons of fresh Struncature or, even, vacuum packed, in front of which the only question you can ask yourself is “why?“.
In these cases the only thing to do is to rely on common sense, which prevents us from calling Struncatura a fresh pasta!