6.10.2019
HISTORY OF VITICULTURE IN CALABRIA
It is not possible to give a complete guide on the history of vines and grapes in Calabria, this history is so full of stories, details, discoveries, that it is easier understand its legacy than understand all the profound assets, present in the wine making.
Contrary to the belief that the vine was imported to Europe from ‘the Far East, many fossil finds in northern Europe and the Mediterranean regions show that since the beginning of the Tertiary appeared in Europe plants belonging to the botanical species “Vitis” , the ancestors of modern “Vines” European.
The fossil record shows us very different plants by modern life, diversity due to climate changes that occurred during the Eocene geological eras, Miocene and Pliocene. Only during the Pliocene begin to appear vines like those presenting today as Vitis Praevinifera Saporta and Vitis Subintegra Saporta.

The findings grape seeds dating back to Neolithic times, make us believe that the European man used the grapes in his diet.
During the Bronze Age have been found in Italy only traces of wild grape, the “Vitis Vinifera Silvestris” and this excludes the possibility that at that time the man would dedicate to growing grapes.
The first traces of vine growing for the purpose of wine production found themselves around 2000 years ago in Calabria and Sicily. The cultivation of grapes in southern Italy was probably developed because of the ancient commercial activities of the Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations Aegean with southern Italy.
MAGNA GRAECIA (SOUTH OF ITALY) AND THE LEGEND OF CIRÒ
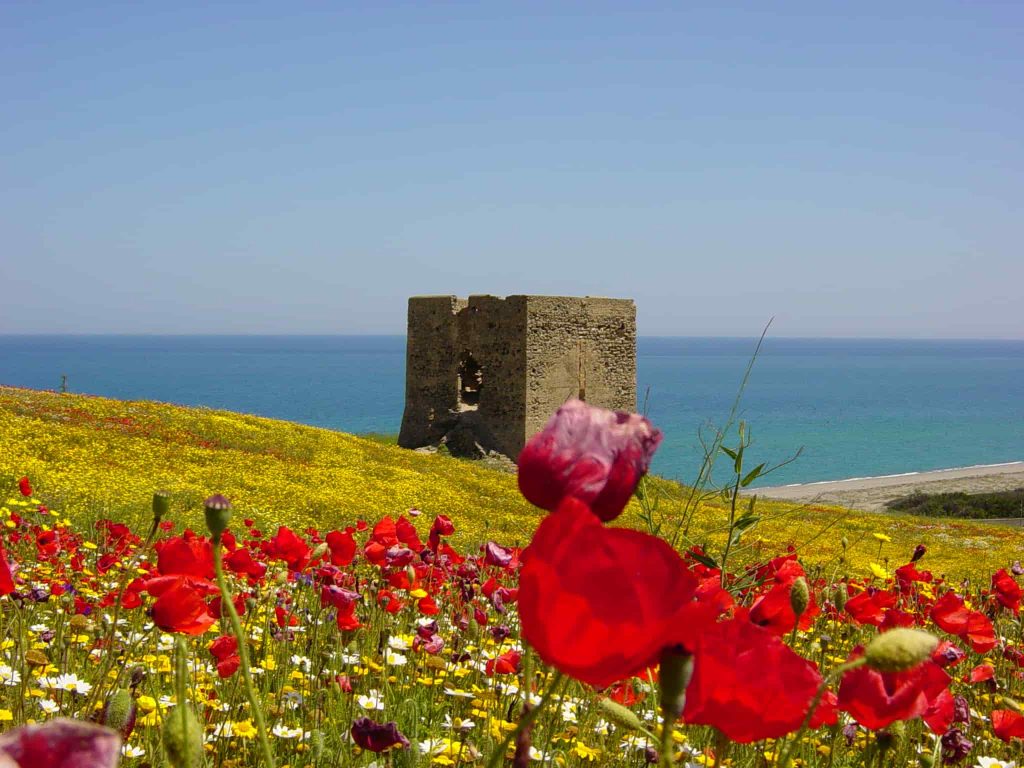
On the Ionian coast of Calabria is Cirò, a small town, where the wine is produced since the time of Ancient Greece (so called Magna Graecia in Calabria).

Legend has it that Philoctetes, return home after the Trojan War, founded the city of Crimissa and Petelia, today’s Cirò and Strongoli. A Crimissa Philoctetes built a shrine in honor of Apollus Aleo, who had healed from the bite of a snake washing his wound with wine. In the area of the cult Dionysus, protector of the screw and of the trees, and expanded rapidly in his honor they took place celebrations in which consumed large amounts of Crimissa wine.
Further, legend has it that during the Olympic Games that were held in Greece, was offered the Cirò wine to the winning athletes. The Ciro wine is now produced in the same places where once stood the city of Crimissa.

VITICULTURE IN ROMAN TIMES
The vine was considered a sacred plant by the Greeks and Romans, and in the regions of southern Italy viticulture never ceased to flourish.
Following the expansion of the Empire and the Roman dominion over the Mediterranean territories, between the fifth and third centuries BC, the rural economy and especially viticulture, underwent profound transformations. Large imports of grain from the new provinces of the empire created a drop in demand and, consequently, a sharp drop in the value of the wheat produced in Italy. Therefore, the large landowners began to revise their agricultural strategies and so the cultivation of vines became one of the agricultural activities more ‘practiced and profitable.

The Romans with the help of Greek and Asian slaves perfected the viticulture and enology. The goodness of Italian wine became well known and his fame opened the way for exports of wine products. The Roman Empire conquered a true monopoly in the production and export of wines that reached its peak in the period between the second century BC and the first century AD, a period marked by many important literary works on viticulture and oenology.
The decline of the Roman Empire and the crisis started from the second century AD and civil wars, the fiscal tightening, the indifference of the landowners and the progressive abandonment of the countryside led to a considerable reduction of the practice of viticulture, to the point that the end of the Roman Empire seemed almost drag even with itself the end of practices of viticulture.

THE MIDDLE AGE AND THE BYZANTINE AGE
Rossano and Santa Severina, located respectively north and south of Cyrus’, were the most important centers of Byzantine Calabria, founded between 700 and 1050 BC. At that time, the Byzantines took possession of many of land once owned the Roman landowners.
Being wine an indispensable element in the Christian rite of the Eucharistic table, the viticulture was practiced by monks within the convent walls, safe from bandits who roamed the countryside.
The wine was used by the monks to Mass, was offered to the visitors and was also used in moderation by the monks themselves.
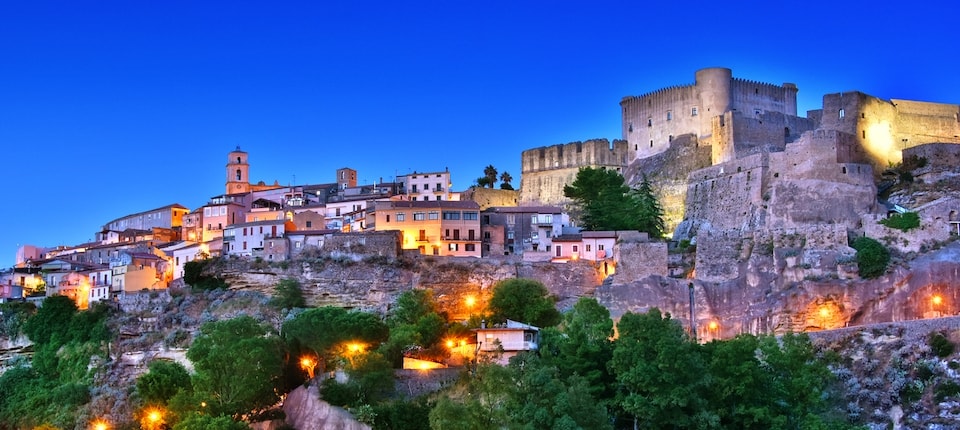

Around the year 1000, deeds of gift, sales documents and agricultural contracts show that the cultivation of the vine was no more exclusive of religious orders, it began to flourish beyond the control of the church. Around 1200 the wine began to be exported to Europe and its use spread so widely that the church found it necessary to take severe measures against alcoholism to the point that, in 1215, Pope Innocent III proclaimed drunkenness as a serious offense.
THE “MODERN” CULTIVATION
In 1868, the vineyards were invaded by a terrible parasite from the new world.
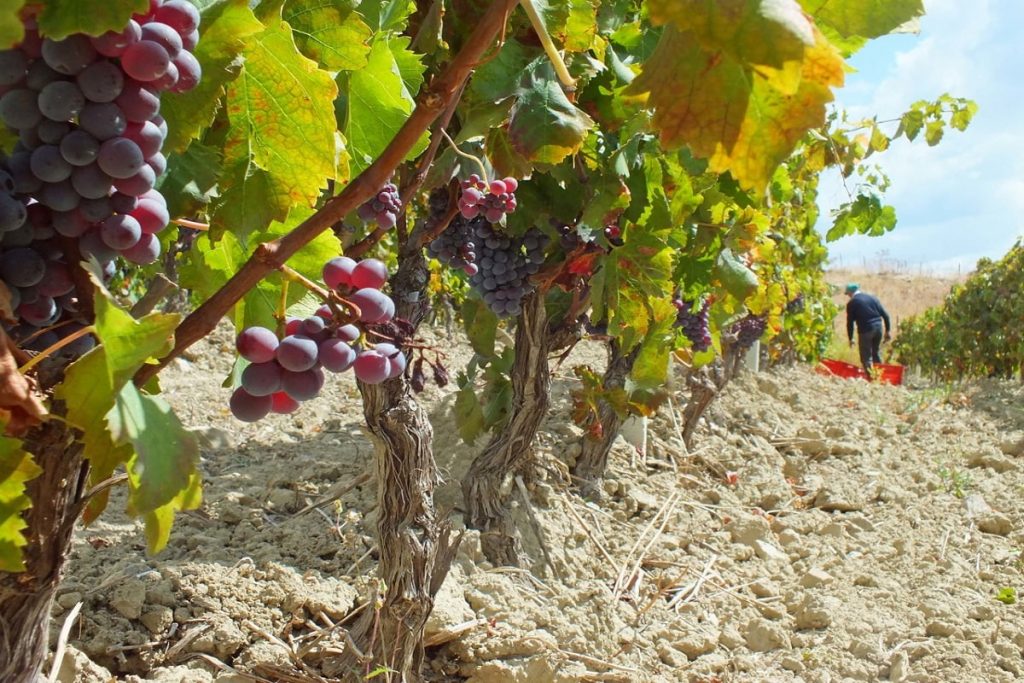

The Phylloxera, a small insect that lived in the land and causing the death of the plants by the bite of the roots, came to Europe through the importation of American vines.

These parasites caused a revolution in viticulture practices handed down from father to son through the centuries: whereas, before, the vines were coming from a single “parent” (a European grapevine), it was then necessary have an American root (resistant to phylloxera), on which was later grafted the European grapevine.
The practices of viticulture then began to be based on new farming concepts, otherwise the vines could not resist the terrible attacks of new enemies, microscopic and relentless.

The vineyards of Cirò were therefore uprooted and replanted using imported from screws, which were used as “rootstocks”, on which were grafted the native varieties of Greek Gaglioppo and White, which are the varieties still used today to produce the best wine Cirò “DOC” (an Italian official mark of quality).
THE FIRST WINE CIRO’ BOTTLED
At the end of 1800 the wine first bottles of Cirò began to be produced in small quantities for local consumption by the noble families of the area, owners of the largest vineyards.
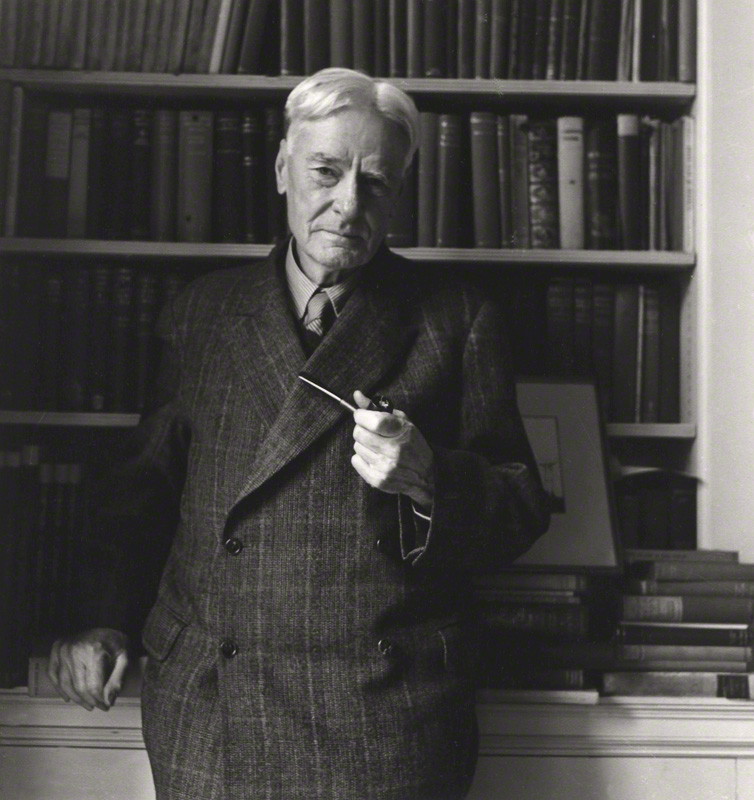

At the same time, some passing travelers in Calabria, including Norman Douglas, began to celebrate in their diaries the exceptional quality of the Wine of Cirò…






